Atenas, Attica, Greece
Suggest Place to Visit
8233
Track to location with GPS |
 |
Ancient Athens was one of the dominant city-states of Greece during the early part of the first millennium. C. Approximately between the years 500 a. C. and 323 d. C. was one of the largest cultural and intellectual centers of the world, and originated many of the ideas, achievements and practices of western civilization, among them the concept of democracy. The defeat against Sparta in the year 431 a. C., the height of Macedonia in the later Hellenistic era and finally the Roman conquest was left with power and prestige to Athens. The end of the era was classic in 529, according to the philosophy schools. During the Byzantine empire Athens entered decay, but the center of Byzantine power in the territory of Greece moved to Mistra. Between the 13th and 15th centuries the city changed hands several times, between the Greek (Byzantine) and the French and Italian horsemen of the Latin Empire, who started to establish a duchy in Athens; Aragonese and Sicilians also occupied the city at various times, and the Duchy of Athens, including Neopatria, was able to be Aragonese. Finally, in 1456 it was conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
Following the population, the population declined considerably, dropping to 4,000 inhabitants at the moment. Athens suffered a Venetian attack in 1687, during the course of General Morossini's Venetian bombing, which was responsible for the explosion of a Turkish powder that ruined the Partenón, and a Turkish response to the next. After the War of Greek Independence (1821-1829) Athens became part of the new Greek State, and was named the capital of Greece on the 18th of September 1834.
Since the creation of the modern Greek State Athens has not sought to increase its economic weight, political influence and population. During the reign of Rey Otón, multiple public buildings were built and the growth of the city was planned. After the Asia Minor disaster in 1921, more than a million Greek refugees from Turkey came to the country, most of them moved to Athens, which resulted in an explosive and disorderly growth. The immigrant oiled oil was produced after the Second World War (during which Athens was occupied by German forces), when the population of many rural areas and islands moved to Athens. A rapid and disorderly growth is occurring again, which is at the origin of the problems of trafficking and contamination that is supporting the city. In September 1999 the metropolitan area of Athens suffered an earthquake that caused 143 fatalities, damage in thousands of buildings and some pieces exposed in the National Archaeological Museum. The major infrastructure works carried out since the entry of Greece into the European Union, especially for the preparation of the 2004 Olympic Games, have partially succeeded in alleviating some problems and improving the quality of life in Athens. Currently the city is the political, economic and cultural center of Greece, and a tourist destination of great international importance.
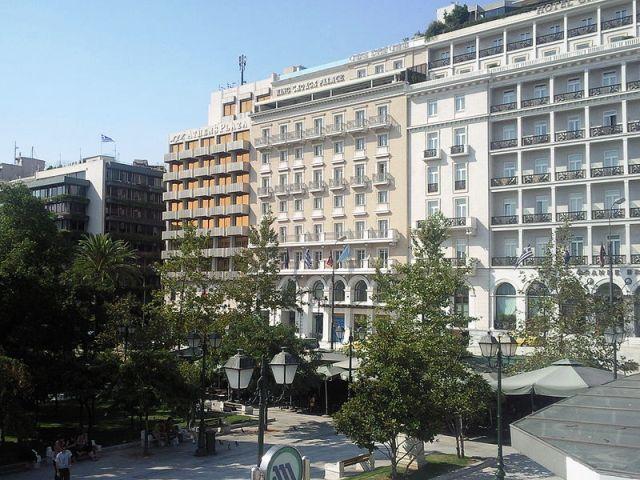
Athens (in Greek Athína) is the capital of Greece and currently the largest city in the country. The population of Athens is 741,512 (in 2001), but its metropolitan area is much larger and comprises a population of 3.7 million (in 2005). It is the main center of Greek economic, cultural and political life.
The history of Athens extends over 3000 years, which suits one of the most ancient inhabited cities. During the classical era of Greece, it was a powerful city that had a fundamental role in the development of democracy. It was also a cultural center where many of the great artists, writers and philosophers of antiquity lived. These contributions from Athens to the thought of their time had a great influence on the development of Greece, Rome and Western culture.
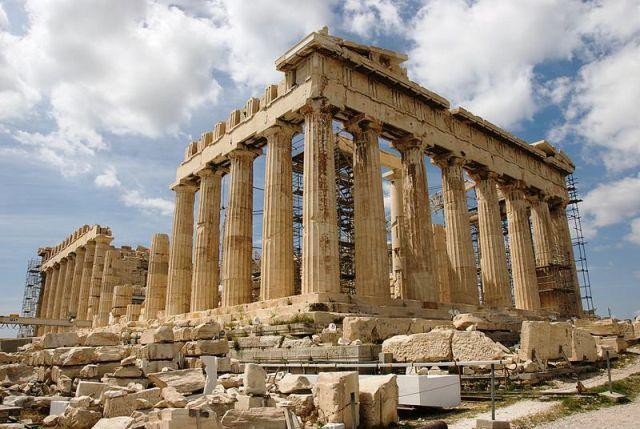
Athens is one of the richest cities and archaeological remains of extraordinary importance, of which most famous is the Partenón en Acrópolis. In addition to classical Greek constructions, Roman and Byzantine monuments are also preserved, as well as several notable modern constructions.
Athens extends over a stretch of the Attica peninsula, limited by the Saronic Gulf; to the west by Mount Egaleo; northwest to El Parnitha; north-east by el Monte Pentélico; and the east by Monte Imitós. The municipality of Athens is located approximately in the center of this language, but the urban expansion of the XX century has just merged with the surrounding settlements, currently considered to be suburbs. At the beginning of the 21st century, this metropolitan area comprises 54 municipalities and occupies practically the entire length of the city. The city of Athens has 38 square kilometers, but with the metropolitan area in short, only 427, converging on one of the biggest cities in Europe, both in extension and in population.
The municipality of Athens is located in the center of the metropolitan area, and contains the main archaeological remains and tourist attractions. This is limited by several suburbs that face the hill of the Imitós, as Zografou y Kaisariani. The northern suburbs, like Maroussi (where the Olympic complex is located), Kifisia, Penteli or Neo Psychiko, tend to be occupied by high classes, but the western suburbs (like Egaleo, Rentis, Haidari or Petroupoli) are more popular. and include industrial areas. Along the long coastline there are several ports, marinas and beaches; some coastal suburbs are El Pireo, Faliro, Glyfada and Vouliagmeni. To the west are the commercial and industrial pubs of El Pireo, but the areas in the south-east and in the center are more oriented at leisure.
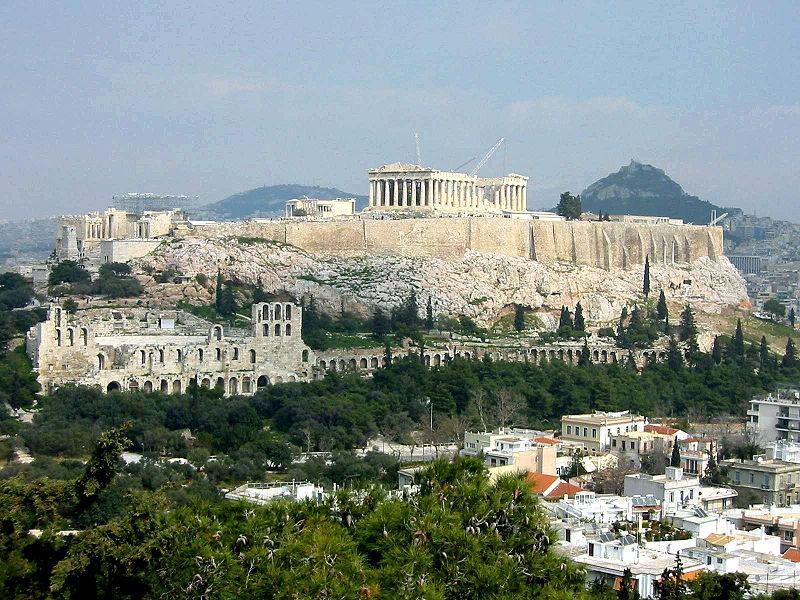
In addition to the four surrounding mountains, in the interior of Athens there are abundant hills, which has an especially abrupt city. The most important ones are: Licabeto, Acrópolis, Filopappos and Tourkovounia; other smaller hills include Arditós, Strefi, Ninfeon, the Mouseion.
The morphology of Athens occasionally causes a phenomenon of thermal inversion, characterized by an increase in air temperature and an increase in altitude. The contamination problem that is usually encountered in Athens is partly due to this phenomenon.
Población
Along the way, the Athens population has evolved in a highly irregular way. After being one of the most important cities of Antiquity, during the Byzantine period it entered into a decay that was accentuated during the Ottoman rule. After the independence of the Greek Greek State was proclaimed in 1834, the population quickly grew, thanks in large measure to the oilcloths of refugees and the rural exodus; in recent years there has also been an increase in immigrants from surrounding countries like Albania. Currently, the metropolitan area of Athens concentrates more than one third of the total population of Greece.
According to the 2001 census, the Athens population was 745,514 inhabitants, and the metropolitan area population was 3.7 million. However, if you think the total population is higher. If it is believed that some residents in Athens originate from other Greek settlements, they register in their native place to conduct the census; asimismo, there is a population of immigrants that is not quantified.
Athens has varied leisure and cultural possibilities.
There are several archaeological deposits that span from the archaic time of Greece to Roman domination. In addition to the great archaeological sites (Acropolis, the Agora, the Cerámico and the Temple of the Olympian Zeus), the places abound in the city where you can see a small fragment of an ancient building: from the Lisícrates lantern to the monument from Filopappos, there are remains of a wall near the central market, a spa in the Amalias street or a vertical section of various archaeological layers in the Syntagma metro station. There are ongoing restoration and remodeling jobs.
The remains from the medieval period up to the 18th century include a large number of Byzantine churches and monasteries of Kaisariani and Dafni. There are many examples of neoclassical architecture of the XIX century and the beginning of the XX, as the so-called neoclassical trilogy.
One of the most outstanding museums in Athens is the National Archaeological Museum, which contains the largest collection of objects and works of art from the classical Greece of the world, including famous pieces such as the funeral mask of Agamenón or the Zeus of Artemision. Other important museums, specialized in other historical periods, are the Museo de Arte Cicládico and the Museo Cristiano y Byzantino. Museo Benaki covers since the Prehistory up to the 20th century. The Acropolis, the Ancient Antigua and the Ceramics also have museums in situ; a new Acropolis museum, equipped with a much larger exhibition space, was opened on June 20, 2009.
Athens has multiple venues for theater, music, exhibitions and shows. One of the most significant events in the Athens Festival, which takes place between the months of May and October and includes performances of opera, dance, theater (especially classical Greek theater) and concerts, using, among other scenes, the odeón theater of Herodes Ático (near Acropolis, built in siglo II d. C.).
Archeology, monuments and places
• Acropolis, with Partenón, Erecteión, Propileos, Atenea Niké temple and museum. There are also remains on the side of the Acropolis.
• Ancient Agora.
• Roman Agora, where you can find the Torre de los Vientos.
• Hadrian's Arch.
• Ceramic, old cementerium located next to the old walls.
• Filopappos Monument.
• Lysícrates Monument.
• Temple of Olympian Zeus.
• Pnyx, a rocky hill near Filopapos and Acrópolis, from where legislative events were celebrated during the Classic Period: es decir, the first democratic parliament.
• The Areópago, a small rocky elevation in front of the Acropolis, where the courts were celebrated during the Classic Period.
• Panathinaiko Stadium, also called Kallimarmaro, a white marble stadium built in 1895 for the first Olympic Games of the modern era, in the same location where the ancient Athens stadium was located.
• Platón Academy.
• Monastery of Kesariani, located on the slope of Monte Imitos, with frescoes of the 16th and 17th centuries, in the suburb of Kesariani.
• Dafni Monastery, declared a World Heritage Site, built over a temple of Apollo.
• Mitrópoli, cathedral of 1862, the first important construction behind the independence of Turkey.
• Panagía Gorgo epíkoos, raised on an ancient temple of Eileitia.
• National Archaeological Museum.
• Museum of the Ágora in Athens, in the reconstructed building of Stoa de Átalo.
• Museo del Cerámico.
• Museo Benaki.
• Epigraphic museum.
• Cycladic Art Museum.
• Byzantine and Christian museum.
• Plaka
• Anafiotika
• Plaza de Monastiraki, where there is a colorful street market and an orthodox monastery that gives its name to the place.
• Psiri, downtown, very popular for nightlife.
• Plaza de Sintagma, the heart of modern Athens, from where the Parliament and the Monument to the Unknown Soldier are located.
• Puerto de El Pireo.
• Olympic Complex for the 2004 Games, in the suburb of Maroussi.
• Jardines Nacionales, date of the XIX century and are located next to the Parliament and the Plaza Syntagma.
• «Neoclassical Trilogy»: three buildings of the XIX century (the Academy, the National Library and the University of Athens), built according to the proposals of the architect Theophile Hansen. They are located in the center of Eleftherios Venizelos (also called Panepistimiou).
• Monte Licabeto.
• Gazi, a former gas factory, converted into a cultural space.
Comments
We don´t have yet any comments about:
Athens
Athens
Be the first to leave a comment as it is very important to inform other people
Outros locais a visitar
Within a radius of 20 km from:Athens
Arco de Adriano |
| 0,0 Km |
 |
Grecia |
| 0,3 Km |
 |
La torre de los vientos |
| 1,1 Km |
 |
Atenea Nike Temple |
| 1,2 Km |
 |
Partenón |
| 1,3 Km |
 |
Monumento Lisicrates |
| 1,5 Km |
 |
Templo de Zeus El Olimpico |
| 1,9 Km |
 |
Acrópolis |
| 2,0 Km |
 |
Hotel reservation near Athens within a radius of 20 km
Why to book with RUTAS TURISTICAS
The best prices
Our partnerships with the world´s largest operators offer research on the best market prices.
More options
At Rotas Turisticos you can book the hotel, buy the air ticket, book the transfer from the airport to the hotel and vice versa, book the local excursions, rent the car, take travel insurance and consult the places to visit and where to go.
Holiday Tips & Destinations
Hundreds of holiday destinations with all the options that allow you to easily choose the destination that best suits your dream vacation.
RUTAS TURISTICAS
Links