Atenas, Centro da Grécia, Greece
Suggest Place to Visit
4565
Track to location with GPS |
 |
Heiress of Ancient Greece, Greece has a long and rich history during which it extended its influence over three continents.
The Aegean coast saw the rise of the first European civilizations, the Cretan or Minoan civilization (in memory of the legendary King Minos) and the Mycenaean. After his disappearance, another resurfaced around 700 a. C. the last one was conquered by Rome in 168 a. C., although the superiority of Greek culture profoundly modified the Roman. In fact, in the eastern part of the empire the culture and the Greek language remained more influential.
The Medieval Greek Empire is constituted as one of the largest empires in the history of Europe; it ranges from the Adriatic Sea and southern Italy to the Middle East; Constantinople stands as the Second Rome and as the center of the heiress civilization of ancient Greece and Rome. The Greek Empire of Byzantium is also one of the longest-lived empires in history: it lasts more than 1,000 years, from the 5th century to the 15th century.
It followed the fall of Constantinople, the capital of the Empire, the entrance of the Ottomans in Greece, as well as in the rest of the Balkan Peninsula. The Greeks lived for 350 years under the Turkish yoke, from which they were released in 1821 thanks to the War of Independence of Greece. Once Greece regained its independence in most of its territory, the modern Greek state was constituted, the nobleman Ioannis Kapodistrias being the prime minister of modern Greece. At the end of the 19th century the Greeks continued to fight against the Turks to continue liberating territories hitherto submitted, such as Thessaly or the Epirus. During the Balkan Wars, Greece also managed to liberate Macedonia and Thrace. In 1922 the Greek invasion of Asia Minor, however, ended in defeat and the expulsion of 1,500,000 Greeks, thus ending 4,000 years of uninterrupted Greek presence east of the Aegean Sea.
During the decade of the 30s, Greece was dragged into fascism by the hand of dictator Ioannis Metaxas. During World War II, Greece was occupied by Nazi Germany under a collaborative regime. The Greek Civil War followed the Nazi occupation, which ended in 1949. In 1952, Greece entered NATO, and in 1981, in the European Union. Today, Greece is a well-established democratic parliamentary republic with considerable economic development.
In 2007 a series of fires devastated much of the forest mass of this country.
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic is a country in southeastern Europe that is part of the European Union (EU).
Located on the south side of the Balkan Peninsula, it borders Bulgaria, the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia and Albania to the north, to the east with Turkey and to the west and south with the Ionian and the Mediterranean.
Greece is currently a parliamentary republic.
• The President of the Republic is elected every five years by the Hellenic Parliament.
• Every four years elections are held to the parliament after which the Prime Minister and his government are renewed.
• The legislative power is unicameral and is represented by 300 members of parliament, who represent the Greek people.
• The judiciary is independent and is represented by three superior courts.
• Greece is governed according to the political Constitution of 1986.
• Greece has been a member of the EU since 1981.
• Enjoy friendly relations with all countries of the world.
• Political parties operate at a national level, unlike other countries, in Greece there is no local party or prohibited party.
Greece is a member country of the European Union (EU) located at the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula on the Mediterranean Sea coast.
Its surface is 132,562 km² including inland waters of the Aegean basin, islands and islets. According to Eurostat demographic studies, the population of this country is 11,244,118 inhabitants.
GEOGRAPHY
Geographically and climate the Greek territory is very varied. With 9,000 islands, islets and rocky outcrops, 15,021 km of coastline (more than 16,000 km of coastline including rocky outcrops), being the second in Europe after Norway and tenth in the world behind the United States in coastal length. The Aegean Sea has been of great importance in the history and development of Hellenistic culture and civilization.
Greece is mostly mountainous and has several chains including the Dinaric Alps to the west (which by means of islands change direction to the southeast to the south of the Peloponnese); Rhodope Mountains, the chain of Olympus among others. Greece is the country in Europe with the highest number of mountain peaks. Its highest height is in the chain of Olympus, on Mount Mytikas 2,919 meters above sea level, this being the fourth in Europe in prominence (real height from the base to the summit) surpassed only by Mont Blanc, Mulhacén peak and Mount Etna . Its height of prominence is 2,919 coinciding with its height s.n.m. since its base is 0 meters above sea level.
The distances of ends in a straight line are SE-NO 993 km and S-N 800 km and its geographical location between parallels 35º N and 42º N.
Agriculture represents a very important role in the economy of Greece. The industries created during the post-World War I period were mostly destroyed during World War II and the following civil war. Since then, the development of the manufacturing sector of the economy has been hampered by the lack of fuels and the difficulties arising from the use of the country's hydroelectric power. In 1970, however, the contribution of manufactures to annual national production exceeded that of agriculture for the first time. Two important sources of income for Greece are shipbuilding and tourism. The extraction of oil from the fields of the North Aegean Sea was a great help for the economy in the early 1980s. Greece became a member of the European Economic Community (today, European Union) in 1981. The national budget a In the early 1990s it was estimated at about 37.6 billion dollars of revenue, and 45.1 billion of spending.
Its industry mainly produces: food and tobacco products, fabrics and fabrics; chemical products, steel industry; mining and oil refining, while its agriculture is based on the production of wheat, corn, barley, sugar beets, olives, tomatoes, wine, tobacco, potatoes; Meat and dairy products.
The organization of unions is union. The members of each guild are affiliated with national federations.
CULTURE
The Greeks, in general, feel a great link with their past, emphasizing the classical period of Greek history, and from the Hellenistic and Byzantine to the present. Both classical and Byzantine Greece represent for most Greeks the precursors of the current Hellenic Republic. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries the ancient borders of the Byzantine Empire, or more specifically those that until this period had preserved Greek populations, came to represent for some an ideal within the reach of the contemporary state. The cultural and linguistic continuity of the Greek people, however, was complicated during its history by external influences, such as that of Christianity over late antiquity, or the lack of pressure at the end of the Byzantine era, are things strongly emphasized by the Greeks today - being as they are, one of the most patriotic nations in Europe, according to Eurostat.
After the revolution of 1821, Greece went through a period of artistic and cultural renaissance. The current Greeks take care of the memories of the years before the revolution, those of the occupation of Greece by the Ottoman Empire, such as those of the "years of darkness", in which cultural development was completely stopped. Despite the evidence to the contrary (in particular with regard to Cretan literature), the resurgence of Greece after the formation of the first Hellenic Republic in 1831 is remembered by a vast majority of Greeks as the "rebirth" of their nation .
The experience of the occupation, that of the Ottoman era and the modern era, has left an indelible mark on the Greek psyche. In the twentieth century, the trauma of the Greek civil war during which the nation became the first theater of cold war, immediately after the Second World War, which led to enormous privations with the Nazi occupation, and the interference of the USA UU. with the creation of the "Colonel Regime", which ruled brutally from 1967 to 1974; all this led to the emergence of the idea of the Ethnos Anadelfon (´Nation without brothers´), emphasizing that the Greeks could only count on themselves and their countrymen.
However, from the mid-1970s onwards, in parallel with Spain and Portugal, and especially after the entry of Greece into the European Union in 1981, the orientation of Greece, and the aspirations of the majority, focused on European mainstream.
Greek cuisine is cited as an example of the Mediterranean diet. It has influences from Italian, Balkan and Middle Eastern cuisine. Some of the most popular local dishes are moussaka, stifado and spanakopita. In Greece people also eat small dishes called meze dipped in sauces like tzatziki; Grilled octopus, small fish, feta cheese, dolmades (rice, raisins and grains wrapped in grape leaves), various legumes, olives and cheese. Olive oil is added to almost all dishes. Among the sweet dishes is galaktoboureko, drinks such as ouzo, metaxa and a variety of wines including retsina.
It should be taken into account, that Greek cuisine is different between different regions on the continent, and also between island and island.
Comments
We don´t have yet any comments about:
Greece
Greece
Be the first to leave a comment as it is very important to inform other people
Outros locais a visitar
Within a radius of 20 km from:Greece
Arco de Adriano |
| 0,3 Km |
 |
Atenas |
| 0,3 Km |
 |
La torre de los vientos |
| 1,0 Km |
 |
Atenea Nike Temple |
| 1,1 Km |
 |
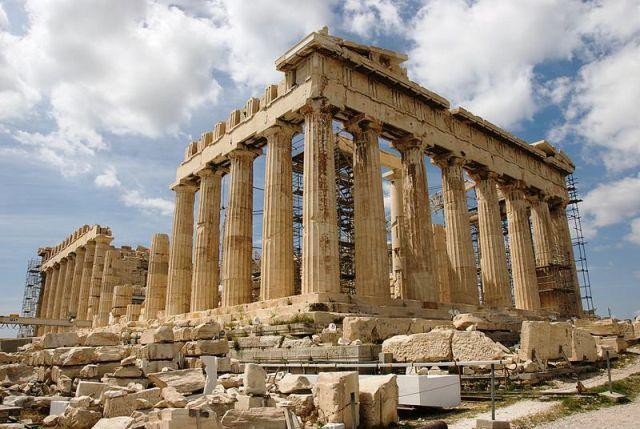
Partenón |
| 1,2 Km |
 |
Monumento Lisicrates |
| 1,4 Km |
 |
Templo de Zeus El Olimpico |
| 1,8 Km |
 |
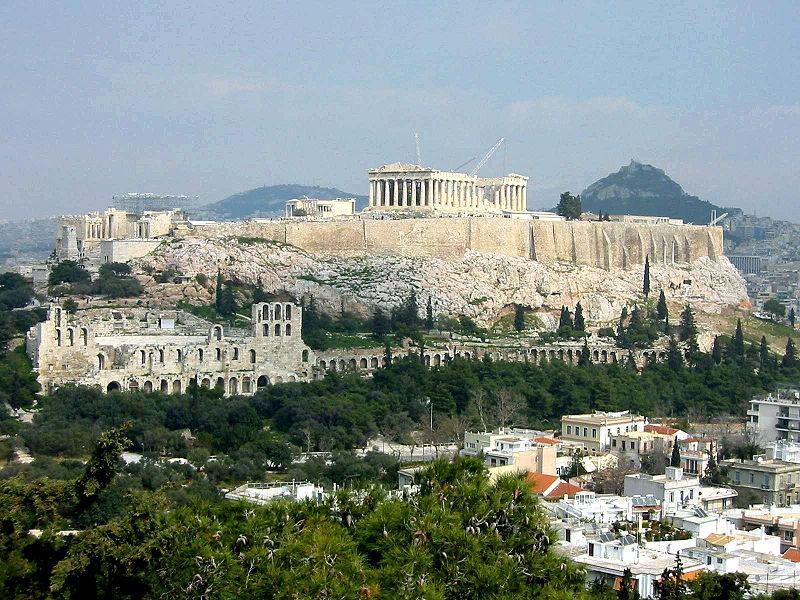
Acrópolis |
| 1,8 Km |
 |
Hotel reservation near Greece within a radius of 20 km
No results
Why to book with RUTAS TURISTICAS
The best prices
Our partnerships with the world´s largest operators offer research on the best market prices.
More options
At Rotas Turisticos you can book the hotel, buy the air ticket, book the transfer from the airport to the hotel and vice versa, book the local excursions, rent the car, take travel insurance and consult the places to visit and where to go.
Holiday Tips & Destinations
Hundreds of holiday destinations with all the options that allow you to easily choose the destination that best suits your dream vacation.
RUTAS TURISTICAS
Links